Lithium Hybrid Organic Battery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lithium hybrid organic batteries are an energy storage device that combines

 V2O5 gels are prepared using the ion-exchange method. Vanadium (V) polymerizes aniline. Before synthesis of a hybrid battery,
V2O5 gels are prepared using the ion-exchange method. Vanadium (V) polymerizes aniline. Before synthesis of a hybrid battery, (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2*6H2O is carried out; this determines the amount of V(V) present in the gel. V2O5*\mathitH2O gel. The following procedure is demonstrated in Figure 3.
V2O5 is used because of its high specific capacity, high
 The cell was prepared by using a working electrode to assemble a half-cell configuration dry
The cell was prepared by using a working electrode to assemble a half-cell configuration dry
lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid el ...
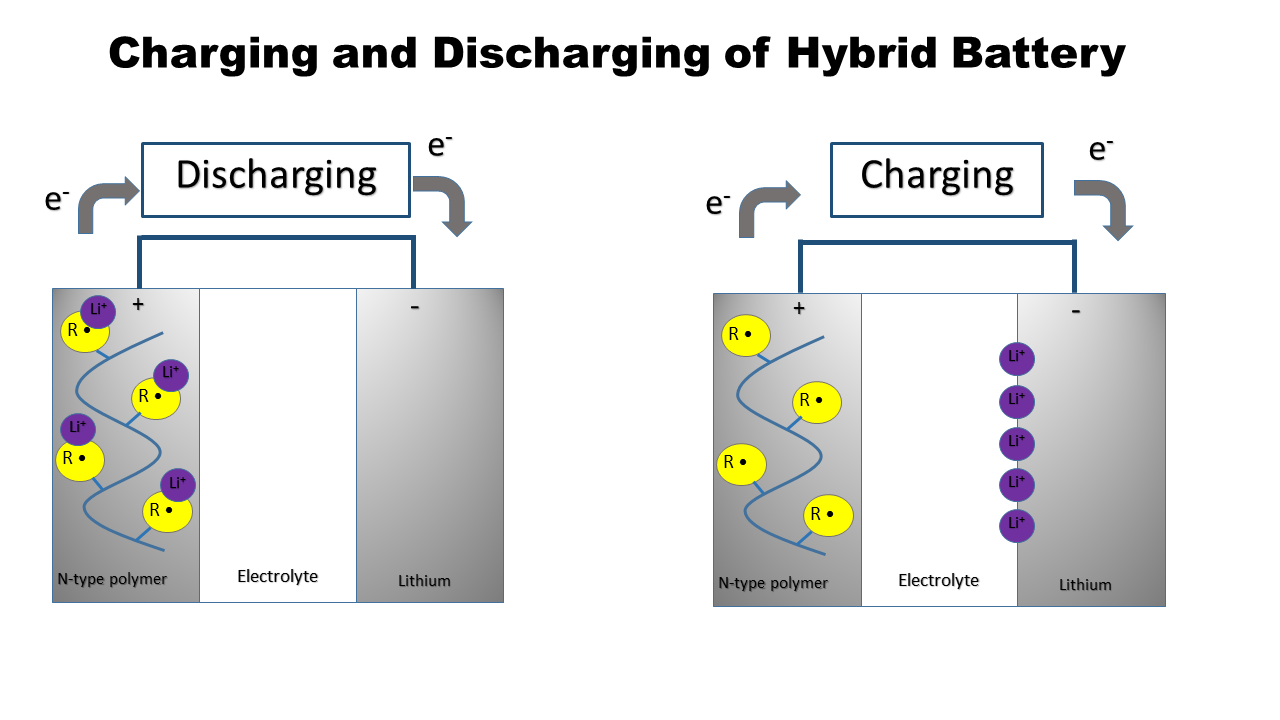
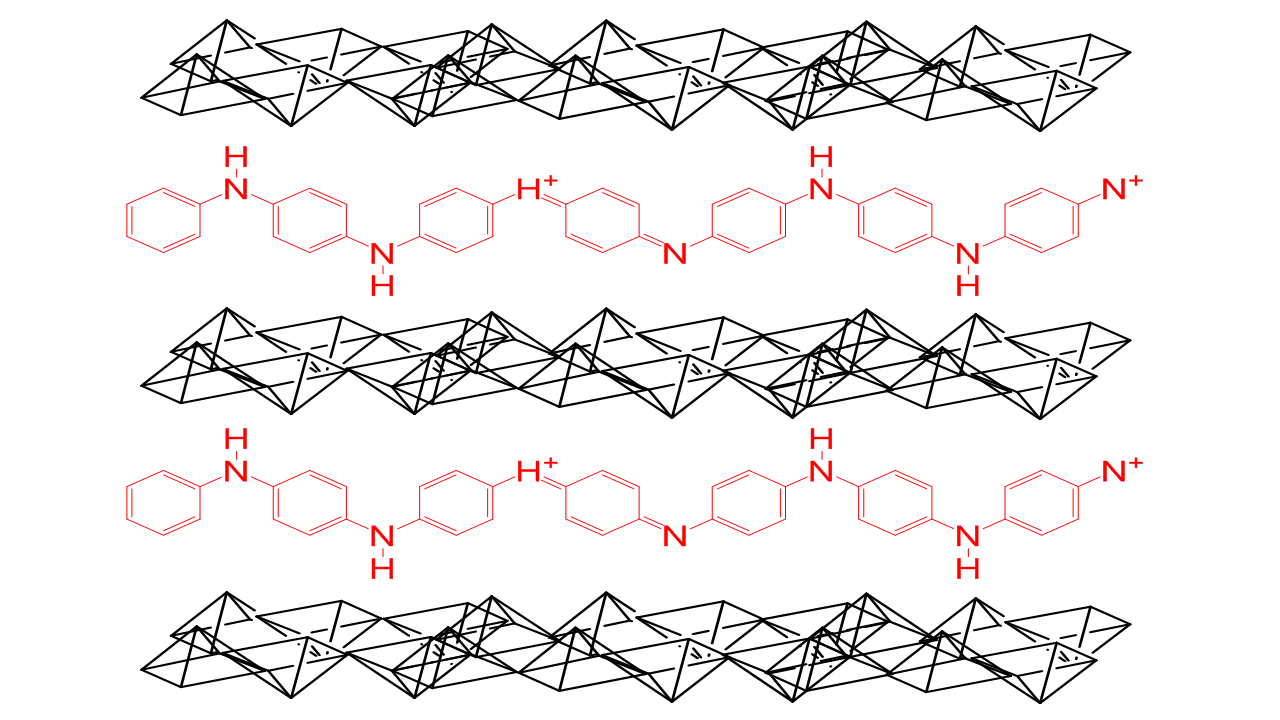
with an organic polymer. For example, polyaniline
Polyaniline (PANI) is a conducting polymer and organic semiconductor of the semi-flexible rod polymer family. The compound has been of interest since the 1980s because of its electrical conductivity and mechanical properties. Polyaniline is one of ...
vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer ( pas ...
(V) oxide (PAni/V2O5) can be incorporated into the nitroxide-polymer lithium iron phosphate battery
The lithium iron phosphate battery (LFP (lithium ferro-phosphate), or Li-IP) is a type of lithium-ion battery using lithium iron phosphate () as the cathode material, and a graphitic carbon electrode with a metallic backing as the anode.
Beca ...
, PTMA/LiFePO4. Together, they improve the lithium ion intercalation capacity, cycle life, electrochemical performances, and conductivity of batteries.
PAni/V2O5
Oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
s, like V2O5, are used as cathodes in rechargeable
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or prim ...
lithium batteries
Lithium battery may refer to:
* Lithium metal battery, a non-rechargeable battery with lithium as an anode
** Rechargeable lithium metal battery, a rechargeable counterpart to the lithium metal battery
* Lithium-ion battery, a rechargeable batte ...
. Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
line V2O5 has a weaker rechargeability or cyclability than amorphous V2O5 because the crystal structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric pat ...
is damaged during discharge/charge cycles. However, amorphous oxides, in particular the V2O5 xerogel
A gel is a Quasi-solid, semi-solid that can have properties ranging from soft and weak to hard and tough. Gels are defined as a substantially dilute cross-linked system, which exhibits no flow when in the steady-state, although the liquid phase ...
, allows lithium ion
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
s to diffuse
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
faster and thus have a better cyclability. Hybrid is formed by combining a conducting organic polymer (e.g. polyaniline
Polyaniline (PANI) is a conducting polymer and organic semiconductor of the semi-flexible rod polymer family. The compound has been of interest since the 1980s because of its electrical conductivity and mechanical properties. Polyaniline is one of ...
) with an oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
(e.g. V2O5).


 V2O5 gels are prepared using the ion-exchange method. Vanadium (V) polymerizes aniline. Before synthesis of a hybrid battery,
V2O5 gels are prepared using the ion-exchange method. Vanadium (V) polymerizes aniline. Before synthesis of a hybrid battery, potentiometric titration
Potentiometric titration is a technique similar to direct titration of a redox reaction. It is a useful means of characterizing an acid. No indicator is used; instead the potential is measured across the analyte, typically an electrolyte solution. ...
of V2O5 gel with Aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starti ...
solution is slowly added onto the thermal stability
In thermodynamics, thermal stability describes the stability of a water body and its resistance to mixing.Schmidt, W. 1928. Über Temperatur und Stabilitätsverhältnisse von Seen. Geogr. Ann 10: 145 - 177. It is the amount of work needed to t ...
, and high structural flexibility with lithium. Up to three moles Moles can refer to:
* Moles de Xert, a mountain range in the Baix Maestrat comarca, Valencian Community, Spain
* The Moles (Australian band)
*The Moles, alter ego of Scottish band Simon Dupree and the Big Sound
People
*Abraham Moles, French engin ...
of lithium ions can be added into the V2O5 lattice to create different structures. The structures created give the hybrid a long battery life. However, the intercalation capacity depends on the moderate electrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allow ...
and low diffusion coefficient
Diffusivity, mass diffusivity or diffusion coefficient is a proportionality constant between the molar flux due to molecular diffusion and the gradient in the concentration of the species (or the driving force for diffusion). Diffusivity is enco ...
of the lithium ions in the vanadium oxide matrix.
Polyaniline is easily produced to have controlled structural and electronic properties. Polyaniline
Polyaniline (PANI) is a conducting polymer and organic semiconductor of the semi-flexible rod polymer family. The compound has been of interest since the 1980s because of its electrical conductivity and mechanical properties. Polyaniline is one of ...
eliminates the coordinated water of the V2O5 xerogel, so more lithium ions can be integrated into the structure. The organic part of the PAni/V2O5 hybrid degrades with the increase of temperature.
V(V) is reduced to V(IV), and aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starti ...
is oxidized to polyaniline. Re-oxidizing V(IV) to a higher oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. C ...
of V(V) increases initial cell voltage and specific capacity. Since polyaniline is an electrochemically active component, it improves the specific charge of the hybrid material. Combining polyaniline with V2O5 yields a larger specific charge difference. Thus, a greater total capacity contribution than V2O5 alone. Furthermore, the hybrid has a higher specific capacity than that of the V2O5 xerogel. Electrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allow ...
is as high as 0.09 S/cm for 15 days.
As a result, PAni/V2O5 hybrid is a conducting network and an electroactive material in the composites, which improves electrochemical behavior. It also prevents the irreversible structural changes made by redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction ...
cycling when the lithium ions enter the lattice. Moreover, this hybrid also has a high specific capacity and improved cyclability without capacity deterioration.
PTMA/LiFePO4
PTMA is an organicnitroxide
Aminoxyl denotes a radical functional group with general structure R2N–O•. It is commonly known as a nitroxyl radical or a nitroxide, however IUPAC discourages the use of these terms, as they erroneously suggest the presence of a nitro group. ...
radical electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials d ...
-active polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
, and LiFePO4 is the inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemist ...
electrode-active material. PTMA is used because it has a high capacity and a long cycle life. To synthesize organic radical-inorganic hybrid electrodes, electrode environments for each component must be optimized. PTMA and LiFePO4 were combined with entire PTMA and LiFePO4 electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials d ...
with different weight ratios: 25/75, 50/50, and 75/25.
 The cell was prepared by using a working electrode to assemble a half-cell configuration dry
The cell was prepared by using a working electrode to assemble a half-cell configuration dry glove box
A glovebox (or glove box) is a sealed container that is designed to allow one to manipulate objects where a separate atmosphere is desired. Built into the sides of the glovebox are gloves arranged in such a way that the user can place their hand ...
with Li metal as an anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
, ethyl carbonate/dimethyl carbonate as an electrophile
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carrie ...
, and a Celgard 3501 membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. B ...
as a separator. Using Arbin BT-200 Battery Tester, the cell was electrochemically cycled at room temperature. By using a Solarton workstation, the cyclic voltammetry
Voltammetry is a category of electroanalytical methods used in analytical chemistry and various industrial processes. In voltammetry, information about an analyte is obtained by measuring the current as the potential is varied. The analytical data ...
and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
Dielectric spectroscopy (which falls in a subcategory of impedance spectroscopy) measures the dielectric properties of a medium as a function of frequency.Kremer F., Schonhals A., Luck W. Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy. – Springer-Verlag, 200 ...
of cells were performed. A focus ion beam-scanning electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
was used to determine the morphology of the electrodes before and after the high rate pulse discharge (HRPD) cycling.
After testing, pure PTMA and LiFePO4 electrode give a sharp redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction ...
peak and decrease the voltage gap between oxidation and reduction.Vlad, A., Singh, N., Rolland, J., Melinte, S., Ajayan, P. M., & Gohy, J. F. (2014). Hybrid supercapacitor-battery materials for fast electrochemical charge storage.Scientific reports, 4. doi:10.1038/sren04315. Therefore, PTMA and LiFePO4 improve the rate and reversibility of the redox couples. Furthermore, the hybrid cathodes have a lower charge-transfer resistance, allowing easier migration of Li ions through the electrode interface. Moreover, PTMA/LiFePO4 has a longer life cycle compared to pure LiFePO4 or PTMA systems.
References
{{reflist Lithium-ion batteries